Natural Law – Overview, History, Importance, Example
Natural law means that human morality comes from nature. Nature law is set of principles of right and wrong which are inherent in nature of the person and not created by the society and judges”
Definition of Morality.
“Your sense of rights and wrong is morality.”
Natural law School
According to this School, there are certain laws which are immutable and eternal. These laws are a constant body of permanent truth’s, unaffected by human beliefs and attitudes. (Also called moral/divine law, law of reason, law of god)
- Natural law based on a prior proposition.
- A priori knowledge, knowledge that is acquired independently of any particular experience.
- A posteriori Knowledge, also called empirical knowledge is derived from experience.
Development of Natural Law.
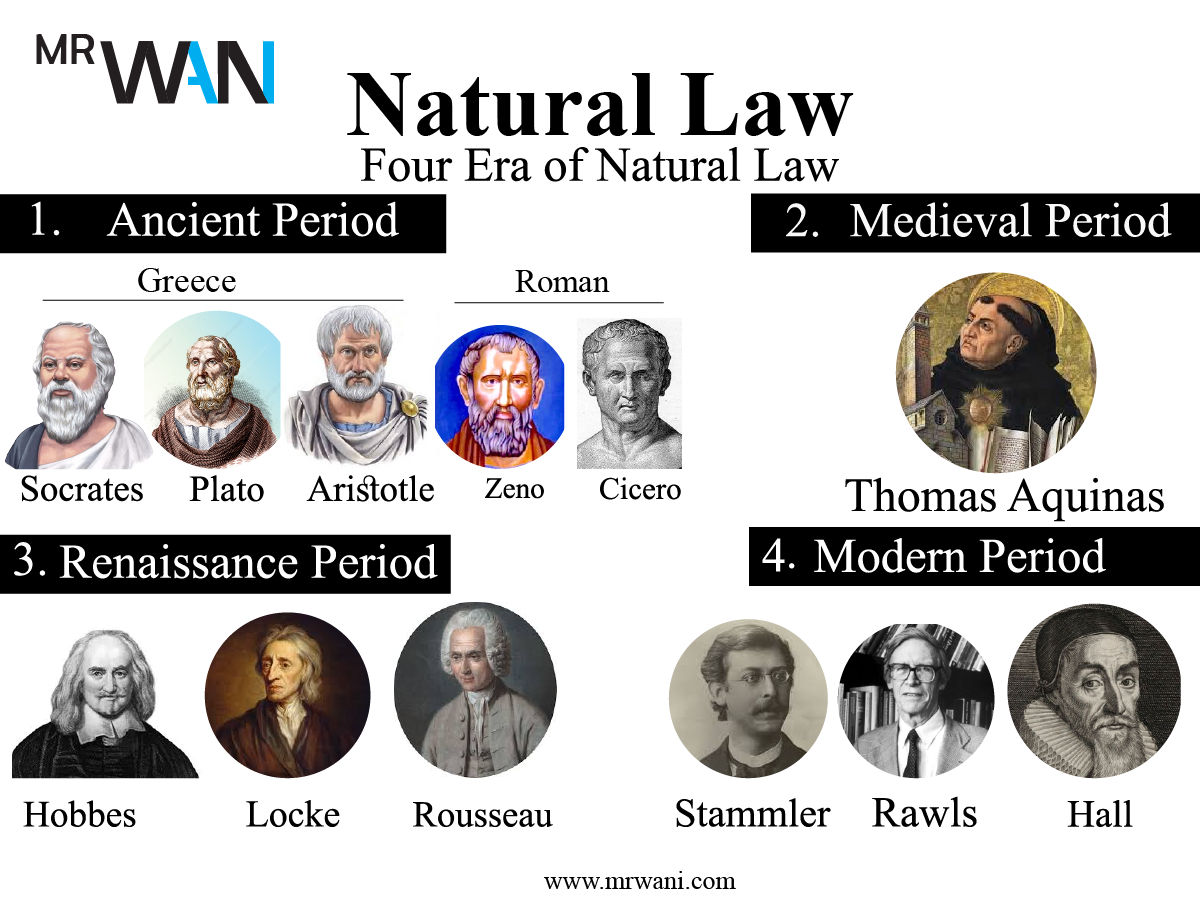
Development of Natural law theories can be divided into 4 time periods
- Ancient Period ( Socrates, Plato, Aristotle, Zeno, Cicero)
- Medieval Period ( Thomas Aquinas)
- Renaissance Period ( Hobbes, Locke, Rousseau,)
- Modern Period (Stammler, Rawls, Hall)
Ancient Period (2000-2500)
Greece (Socrates, Plato, Aristotle)
There is teacher and student relationship between Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. Socrates is the Teacher of Plato and Plato is the Teacher of Aristotle
-
Socrates
- Defined “Virtue” which basically was the concept of good.

- Every man possessed virtue according to which he can critically evaluate the positive law.
- Developed a way of teaching called the Socratic Method, in this method students learn through the use of critical thinking, reasoning, and logic.
- This Technique involves finding the holes in their own theories and then patching them up.
- Our, current “Scientific Method” is inspired by the “Socratic Method”, but for his efforts, in 399 BC, Socrates was put on trial and executed for “Corrupting young and believing in strange god.”
-
Plato
- Student of Socrates, the world knows about Socrates through Plato’s Writing.

- Gave the “Doctrine of Forms”, Forms are transcended archetypes that exist independently of physical world, independently of physical world, independently of human mind, independently of space and time.
- This concept is known as “idealism” ( believing in or pursuing some perfect vision or belief)
- For Plato the forms of “goodness”, “virtue”, “Honesty”, were eternal and immutable because they are given to all men equal measure so that men can have a sense of justice.
- Famous Works of Plato
- The Trial and death of Socrates
- The Republic
- Apology
- The Symposium
-
Aristotle
- Aristotle was as student of Plato for 20 years but rejected the doctrine of forms by Plato.

- Aristotle rejected Plato’s theory of forms but not the notion of form itself.
- For Aristotle, forms do not exist independently of things-every form is the form of something. A “substantial” form is a kind that thing would be of a different kind or would cease to exist altogether.
Rome (Zeno, Cicero)
-
Zeno
- Was one a wealthy merchant but lost everything, was reading Socrates and became interested in philosophy.

- He founded Stoicism (the word originated from “ stoa Poikile” a building where zeno studied with his students), his followers were known as stoics.
- The Roman Empire was influenced by stoicism and thus paid high tribute to “Natural Law” because stoicism was basically a branch of natural law theory.
- Romans made three divisions in law on basis of Natural Law Theory.
- Jus Civile (Civil law for roman citizens only)
- Jus naturalis(Principle of natural law)
- Jus gentium (rules applied to foreigners made by magistrate on basis of principles of natural law, also one of the first forms of international law.)
- Cicero
- Roman Philosopher, started that law is the highest reason, implanted in nature, which commands what ought to be done and forbids the opposite.
Medieval Period (10th -12th Century)
- Catholic philosophers and theologians of the middle ages gave a new theory of “Natural Law”.
- Though they too gave it theological basis, they departed from the orthodoxy of early Christian Fathers. Their views were more logical and systematic.
- Thomas Aquinas was the most prominent Natural law Philosopher in this time period.
- Thomas Aquinas
- He divided the law into four stages.
- Law of God
- Natural Law (Revealed through “reason”)
- Divine Law (Law of Scriptures)

- Human Laws (Positive Law)
- Natural law is that part which reveals itself in natural reason. This is applied by human beings to govern their affairs and relations.
- For divine law Church is the authority to interpret it. He basically strengthened the church’s position by giving reasoning to hat was earlier just faith. Strengthened the supremacy of church by giving a rational argument in favor of religion and church.
- According to Aquinas positive law must conform to natural law, positive law is valid only to the extent to which it is compatible with natural law.
Renaissance Period (14th -17th Century)
- This Period of the the Renaissance in the history of development of Natural law may also be called the modern classical era which is marked by rationalism and emergence of new ideas in different fields of knowledge.
- A very important theory which emerged in this time period was the ‘Social Contract Theory’
- According to this theory there is a ‘state of nature’ in which there are no rights and no duties on anyone, then humans came together and formed a ‘Social contract’ that is basically a contract that everyone has certain rights and those rights are enforced by putting certain duties on everyone. A simple example is that everyone has right to life, so every person has duty to not kill.
- Three Main Philosophers of Social Contract Theory.
- Thomas Hobbes
- John Locke
- Jean-Jacques Rousseau
-
Thomas Hobbes
- In his state of nature man always had a fear of instant death, it was a horrible place to live in.
- So, people formed a social contract and gave all the power to a ‘state’ which become the sovereign and responsible for providing security for everyone’s right to life and an order among all in the society.

- His book ‘Leviathan’ argues for a social contract and rule by an absolute sovereign. Hobbes wrote that civil war and the brute situation of a state of nature (“the war of all against all”) could only be avoided by strong, undivided government, so the strong invincible creature leviathan’ is the government here.
- Hobbes’sHobbes theory of natural law supports the idea of absolute authority of the sovereign i.e. a super stable and secure government.
- Famous Work of Thomas Hobbes
- Leviathan
- Behemoth
-
John Locke
- Locke focused more on individualism, in his social contract, people don’t give all their rights to
 the ‘sovereign’ but only a part of their rights, and Locke supported individual liberty and focused on right to property and liberty with the right to life in his state of nature.
the ‘sovereign’ but only a part of their rights, and Locke supported individual liberty and focused on right to property and liberty with the right to life in his state of nature. - Unlike Hobbes, Locke was of the opinion that the sovereigns should not be unlimited. The individual should be able to protest against the government and overthrow it , if the government is not able to protect the individual’s rights.
- Famous Work
- Two Treatise of Government.
- Locke focused more on individualism, in his social contract, people don’t give all their rights to
-
Jean- Jacques Rousseau
- According to Rousseau man entered into a contract in order to preserve the rights of equality and freedom, the surrendered their rights not to a single individual but to the community as a whole which Rousseau calls it was the general will.

- Theory of General Will
The General will is of all people, so you should obey it because it is in a way your will too. The government and laws both should be adhering to the general will, interest of community is more important than interest of individual according to Rousseau.
- Famous work
- The social Contact
- Confessions
- Discourse on Equality
Modern Period (19th -21st Century)
- Many Famous 19th century philosophers did not buy the concept of a priori knowledge, i.e. there are certain immutable truths.
- David Hume said that natural laws says that values are inherent in nature, which is not true, the values and also the concept of justice varies a lot from place to place, if there would have been a perfect, complete system which can be discovered by man then there won’t be so many divergent interpretations of law thought out the world.
- Bentham described natural law as “Simple nonsense; natural and imprescriptible rights, rhetorical nonsense, nonsense upon stilts.”
- Austin didn’t believe in any natural rights, according to him all rights are created by state and enforced by stat. Didn’t acknowledged the social contract theory, he said the people did not consented to obey the state, the state forces them to obey the commands of the state and commands of state are the law.
- In 20th century there were certain attempts to revive Natural Law.
- Because it was felt that there is need for some basic values and standards for society, it was realized that society would always need an ideal of justice.
-
Stammer (1856-1938)-
- was an exponent of ‘Natural law with a variable content’ which is hybrid theory between
 analytical and natural law school.
analytical and natural law school. - According to him there is technical legal science and theoretical legal science.
- For one relates with the content of law, second one relates with the ultimate principles of law
- So basically, law can be different for different societies which will be based on a posteriori knowledge, but the ends to be achieved by those law are ascertainable by the a priori method.
- was an exponent of ‘Natural law with a variable content’ which is hybrid theory between
-
John Rawls (1921-2002)-

- In his book ‘A theory of justice’ also tries to find a middle ground between utilitarianism and natural law theories by using hypothetical concepts of ‘Original Position’ and ‘veil of ignorance’ to determine the structure of society.
-
Jerome Hall (1901-2002)

- He was of the view that it is time to reunite all disciplines. Jurisprudence should be ‘adequate’ in the sense that it will combine the Positivist, Naturalist and Socialist study of law he termed this ‘integrative jurisprudence’
What is Law according to different jurists kindly visit this link.https://www.mrwani.com/what-is-law-definitions-of-law-according-to-different-jurists/