The history of South Asia, especially India and the Delhi Sultanate
South Asia is a vast region comprising six countries, including India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bhutan. The history of this region dates back thousands of years, and has witnessed the rise and fall of many civilizations, empires, and cultures. In this article, we will discuss the history of South Asia, especially India and the Delhi Sultanate, in detail.
Delhi Empire
The Delhi Empire, represents an important historical period. The city of Delhi consists of two parts: Old Delhi and New Delhi. In Old Delhi, the historic buildings, castles, palaces and mosques of the Muslim era are present, while New Delhi was built in the British era and is now the capital of India.
The Delhi Empire started in 1206 by Qutbuddin Aibak, which made Delhi its capital. Earlier, the area was under the influence of Ajmer.
Ancient history of India
It is unclear about India when the region is, ever since the world, this region has existed. Who was the first human being? One of the notions about this is that the first humans were settled in Africa, and from there they moved to different parts of the world. This theory is presented under Evolution Theory, which is the theory given by the British.
Introduction to the theory of human history
Theory evolution (Evolution Theory)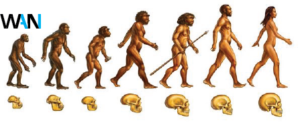
This theory believes that man has come through different periods in today’s form. There was ape (monkey) -like creatures before humans, time. With evolution, he became human. Our scientific name is “homo sapiens”. ” before us there were creatures like “Homo erectus and” Neanderthals “.
The beginning of life
According to the theory of evolution, life began in water. Single-Celled Organisms were born in the water, which later became converted into multi-capable organisms. Then in the water, insects, fish, (small fish, large fish, spinal fish), and other aquatic organisms came into being. The spinal fishes began to live on the dryness, which evolved the drought animals. This process covers millions or millions of years.
Dynamors came into being because of the dryness of the fish. Over time, the creatures changed and different species came into being. Ultimately, monkey -like creatures came into being, which were intelligent and changing different forms. Finally, homo sapiens came into being. One of them “Homo Sapiens”, which are our ancestors. Homo Sipans are about 10 to 15 thousand years old, but human -like creatures exist millions of years old.
If the remains, bones, etc. are found from anywhere in the world, then they assume that they were not human, their head bones and physical structure are very different from the present human beings. So it was a middle creature before humans. These creatures represented the evolutionary stage between the monkey and the human being. These were intelligent creatures, who knew to hunt and were capable of making weapons.
Religious Theory of Creation
If we talk about the Religious Theory of Creation, then all human beings are the descendants of Adam (P.B.H.M). According to the religious belief, Allah created Adam (P.B.H.M) directly in human form. Then his wife Eve was created from the body of Adam (P.B.H.M). Adam (P.B.H.M) and Eve (P.B.H.M) lived in Mecca, and from here human civilization began. According to the Holy Qur’an, the first house built for Allah was the Ka’bah in Mecca, which was founded by Adam (P.B.H.M).
Adam (P.B.H.M) and Eve (P.B.H.M) lived in Makkah, but when they had children, they moved to Palestine. His children resided in Palestine, and from here the spread of human race began. Between the two rivers of Palestine, the river Dajla and the Euphrates, large human populations came into existence. Major cities were built between these rivers, in which great civilizations like Babylon and Babelone flourished.
Yemen is also mentioned in history, where the empire was established. If Nimrod was talked about, the Yemeni and Saudi Arabian border was the kingdom of Nimrod, which was a powerful king of Ibrahim’s (P.B.H.M) era. Egypt is also historically and religiously mentioned, especially in the era of Joseph, when Egypt was the center of a great civilization. The ancient history of human history is the center of civilization. Palestine is considered to be Palestine.
The history of the subcontinent
If we talk about the history of the subcontinent, we can guess what happened here in the past. We need old books to guess. If books are not available, we can use other sources of knowledge of history.
Sources of acquiring knowledge of history
- Our basic sources to learn the history include books, stories, ancient dialogue, buildings, ruins, and human remains. There are stories of learning of history, stories that move from generation to generation. These stories protect thousands of years of history within themselves. Although these stories are not in writing, they are also an important source of history.
- Ancient mirrors and buildings are also an important source of history.
- Ancient buildings, called “ruins” in English, provide us with valuable information about the past. These ruins tell us what civilizations and societies were present in the past.
- Human remnants, such as skeletons, utensils, jewelry, and weapons, are also the main sources of history. These things tell us about the daily life of the people, their lives, and their culture.
In ancient times, books were not in the same form as today. In the past, if a king, chief, or historian wanted to write something, he was engraved on stones. For example, sacred books like the Toraht and the Zaboor were also written on stone plates. The books that Moses received from Allah were also written on stone plates. These stone frames and writings are also an important part of history.
- Another source of knowledge of history is the memorial minarets and buildings of the kings. When a king was crowned or he conquered an area, he used to build minarets or buildings as a monument. The monuments of these victories are still present all over the world today and are an important part of history.
Today, when we guess about an era, we use all these sources: books, stories, ancient texts, ruins, human remains, and memorable buildings. All these things together give us a picture of the past and complete the knowledge of history.
The source of knowing history in the present era
Today, when we guess about the past, the books we have for it are the main source. Books written in the past, stories, which we have heard from our ancestors, are all sources of history for us. In addition, ancient buildings, ruins, and destroyed buildings are also an important source of history for us.
Products used in human life, such as utensils, jewelry, tools, hunting weapons, or travel equipment, are also an important part of history. These things tell us about the daily life of the people, their lives, and their culture. During the kings’ periods of stones, the minarets made in the monument of victories, and when a man of ancient times did not come to read them, the pictures made in the caves of these human beings are also important sources of history.
The history of India (subcontinent)
When we talk about the history of India (subcontinent), we find the oldest religious books of Hindus. Some of these books are more than eight thousand years old. These books, written in the history of India, are primarily Vedas, which are Hindu religious books. Historical books are not so old, but Veda is an important part of India’s ancient history. No one has written by a single person, but they have been written by different people in different periods. There are six major Vedas in Hinduism, which are an important part of Indian history and culture.
Mehrgarh
If viewed in terms of victories, there are some ancient buildings and ruins in India, which are three to four thousand years old. These buildings and ruins give us valuable information about the past. These ruins are very important to understand the history of India. The oldest ruins in the history of India are located in present Pakistan. Mehrgarh, found in the area of Sindh and Balochistan, is the center of the oldest civilization in Indian history. The civilization of Mahargarh is almost as ancient as Egypt’s civilization. We have the pyramid of Egypt about Egypt’s civilization, which is five thousand years old. Similarly, the civilization of Mahergarh is also very ancient in India. Mahargarh is an ancient village, where there are broken buildings and ruins. There are the foundations of ancient buildings, but the above buildings are not left. Whenever a new building is built, its foundations are dug first, and then the building is built on it. The same is the case in Mahargarh, where the foundations of old buildings are present, but the buildings are not left.
During the excavation in Mahargarh, some of the ancient inhabitants were found, made of clay and stone. The civilization of Mahargarh is considered more than five thousand years old, which makes it one of the oldest civilizations in the history of India.
Mohan Jo Daro and Harappa

After Mahargarh, there are two more important historical sites in India: Mohan Jo Daru and Harappa. Both places are an important part of the ancient history of India. Mohan Jo Daru, which is located in Sindh, while Harappa is near Sahiwal, the city of Punjab. Mohan Jo Daru, means “city of dead people” in Sindhi. The city was discovered during the British era, when India was occupied by the British. Before that, no one knew about this ancient civilization. Harappa was similarly discovered by archaeologists. These two places are known as the civilization of the Indus Valley.
The cave of Ajanta and Alorah
Apart from Mohan, Daru and Harappa, the caves of Ajanta and Alorah are also of historical importance in India. In these caves Ajanta and Alrah, the goddesses, kings, and animals are made of idols and pictures. In Janta there are idols of goddesses and kings, while Alorah has pictures of old kings or animals. These caves reflect the ancient history and culture of India.
India is such a large country in terms of area that it has old castles, palaces, and ruins. Many of these places have not yet been fully discovered, and much has to be known about them. In India, families of big kings have passed, whose history is very wide and complex.
In particular, there are five important places in the history of India, Mohan Jo Daru, Harappa, Ajanta, and Alra, which provide us with valuable information about ancient civilizations. These places are the main sources for understanding the ancient history of India.
We can guess what happened here. While current books, which are available to us, we also find valuable information about ancient history. We will also talk about these books in detail.
Etymology of India
The word “Hindu” research
There are different concepts about the word “Hindu”. The term “Hindu” was given by the Arabs. When the Arabs came to India, they called the tribe on the banks of the Indus River a “Hindu”. This word later became a religious term. People living in India were called “Hindus”, and later the word was religiously defined.
The Indus River, also known as “Indus” or “Indus”, is the largest river in this region. It is one of the largest rivers in the world, though it is not as big as the Nile or the Amazon River. The source of the Indus River is in China, and it plays an important role in the history and civilization of our region.
The Indus River starts in China and passes through occupied Kashmir after entering India. It enters Gilgit -Baltistan, then reaches Sindh and Balochistan through Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. The Indus River finally fell into the sea by touching all the provinces of Pakistan. All the rivers in Pakistan, they all join the Indus River. The Indus River is also known as “River Abbasi”.
In the name of the Indus River, the region was named “Sindh”. The land of Sindh was known by different names in different languages. The word “Sindh” became “Hindu” after various accents and changes. Basically, the word was “Sindh”, but over time it became “Hindu” through various accents and changes.
The word “Sindh” became called “Hindu”, and the residents of the Indian area became known as “Hindu”. Basically, “Hindu” was not a religion, but the word was used for people living on the outskirts of the Indus River. Later, when Muslims came to the region, their own religious identity was established. Before the Muslims arrived, all the people in the region were idolaters, called polytheists. His identity was idolatry, and he was called “Hindu”.
When the Muslims came, they established their religious identity, and Muslims and Hindus were separated. If viewed in order, everyone living in India was a “Hindu”. Being a “Hindu” did not mean that he was a Muslim, Sikh, Christian, Persian, Jewish, or Buddhist, but it meant only that he was a resident of India. Just as everyone living in Kashmir is Kashmiri, or every person living in Pakistan is Pakistani, so everyone living in India was “Hindu”. It was a geographical identity, but religiously “Hindu” identity was connected to idolatry.
Nowadays, “Hindu” is known as a religion, based on polytheism. If you read a comparative religion, you will find that “Hindu” refers to those who worship idols or accept anyone other than Allah. It has become a religious identity.
In the past, the word “Hindu” was used for the inhabitants of the region, especially for people living around the Indus River. After partition India in 1947, Pakistan came into existence. Basically, Pakistan was also part of Greater India. Today’s Bangladesh, Pakistan, and India were part of the greater India at some point. Similarly, Nepal, Maldives, and Bhutan were also part of the region.
Conclusion
Where did the ancient inhabitants of the Indus Valley civilization go? How did this civilization destroy? Did the punishment of Allah be revealed, a flood came, or did they die and die? Did a pandem spread, or did they leave the cities and go? History is silent in this regard. There is no clear information about Mohan Jo Daru who lives and people living in Harappa. Their bodies are not there, which seems that the city was not destroyed, but people migrated from here for some reason.
India’s oldest natives
Cole, Bhil, Drawr
The oldest of India included “Cole” and “Bheel”. Cole was India’s oldest inhabitants, living in southern India. These people were black and physically strong. The Dravid Valley was a resident of the Indus, who were of the wheat and were tall.
Current tribes
After Coal and Bhil, the number of Gujar tribes in India is the highest. Gujjar is not ancient in India, but he emigrated from South Asia.
The Rajput tribes are also not ancient in India. He came to India from Central Asia and was the winners. Both Rajput and Jat are the original Central Asia. In India, Sadat and Qureshi are also descendants of external invaders. The Shen’s tribes in Gilgit -Baltistan are the Arabs, while the minister and the Pathan tribes have come from Afghanistan.
The present Indians include Afghan, Iranian, Arab, Uzbek, Turkmen, Kyrgyz, Mongol, and Chinese tribes. Most of the people living in India are the descendants of the external invaders, who came here and settled in different periods.
Read More

Your words have a certain weight to them — they sit with you, long after you’ve finished reading.